Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster (0623–0659)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: There has been significant work developing questionnaires to find effective and reliable ways of characterizing the functional status of patients, to track disease progression and to measure response to treatment. However, these are often lengthy and difficult to perform, especially via telemedicine. We studied whether a VAS response (0-10) to a single question (Physical Function: “PF”): “We are interested in learning how your disease is affecting your ability to function in daily life” could replace the MDHAQ-FN (FN), MHAQ, HAQ-II to reliably predict the functional status of patients with rheumatic disease.
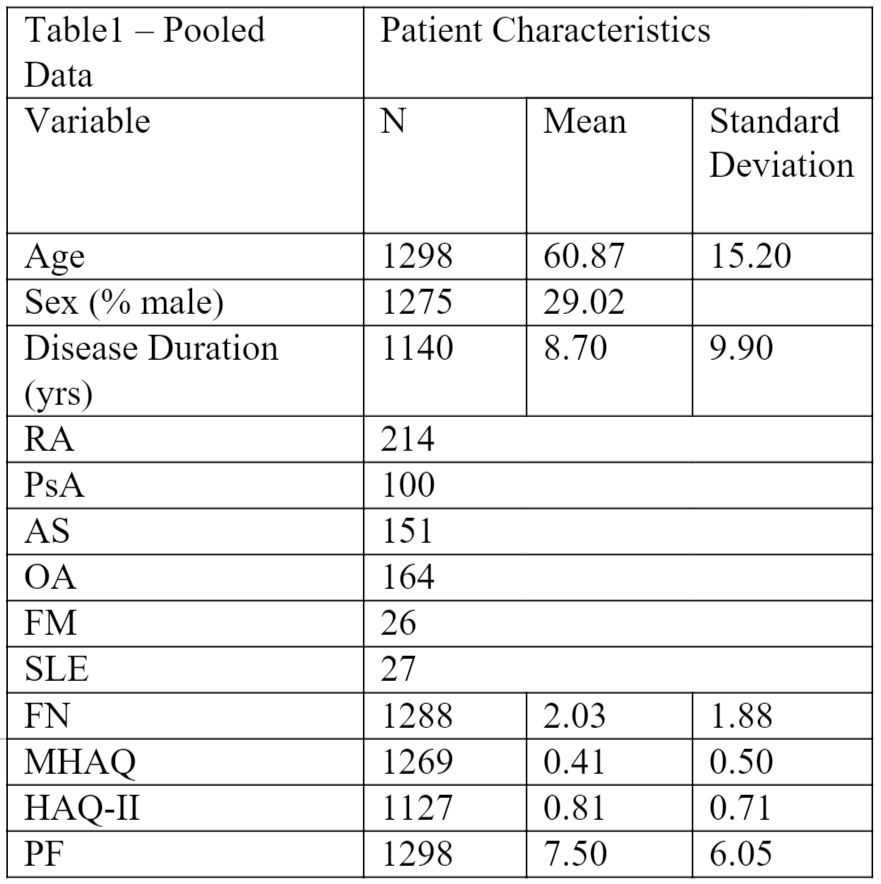
Methods: Pertinent data for adult patients with rheumatic disease collected as part of the routine practices from both a single private practice and an academic site was reviewed. Patients were asked to complete the MHAQ, FN, HAQ-II, and the single question. MHAQ is composed of 8 ADL items. FN is the functional component of the MDHAQ composed of the MHAQ plus 2 additional items. HAQ-II is composed of 10 ADL items. MHAQ, FN, and HAQ-II are scored by taking the mean item score, range 0-3. Spearman’s correlations were used to compare scores from the MHAQ, FN, HAQ-II and the PF. All calculations were performed using Stata Software v14 (Plano TX). IRB approval was obtained.
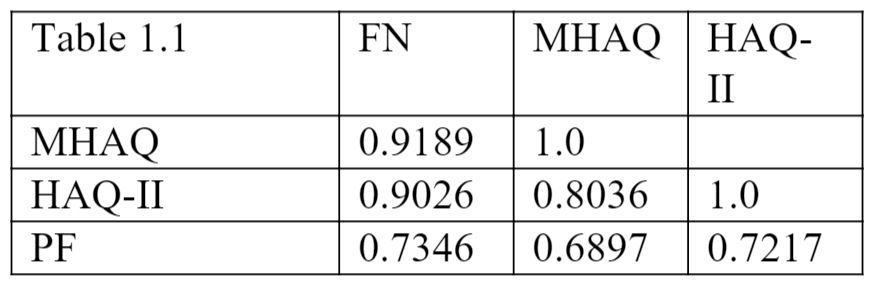
Results: 1,298 patients (29% male, mean age = 60.87 years, mean disease duration 8.7 = years) were analyzed. Patient characteristics are presented in table 1. The FN, MHAQ and HAQ-II all had a very strong correlation to each other. The PF correlated strongly to scores of the FN, MHAQ and HAQ-II (Table 1.1). These correlations were generally maintained, regardless of the underlying diagnosis. Similar results were found at the UNMC.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the utility of the PF: “We are interested in learning how your disease is affecting your ability to function in daily life” as a substitute for the FN, MHAQ and HAQ-II, questionnaires that have previously been validated as effective measures of functional status. The results were comparable, regardless of the underlying diagnosis. This single question is quick to administer and easy to score. In a time when telemedicine is becoming more prevalent, finding efficient and reliable ways of monitoring patients’ wellbeing has become more important than ever. Incorporating this single question into general rheumatologic practice, in conjunction with other clinical tools, such as physical exam and lab values, can help streamline the collection of important data without sacrificing quality of care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Healy A, Fares J, Bergman M, Michaud K, Petro A, Sayles H. Correlation Between the Functional Component of the Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (FN), Modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (MHAQ), Health Assessment Questionnaire II (HAQ-II) and a Single Functional Question (PF) in Patients with Rheumatic Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation%e2%80%afbetween%e2%80%afthe-functional-component-of-the-multidimensional-health-assessment-questionnaire%e2%80%affn-modified-health-assessment-questionnaire%e2%80%afmhaq-health-asses/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation%e2%80%afbetween%e2%80%afthe-functional-component-of-the-multidimensional-health-assessment-questionnaire%e2%80%affn-modified-health-assessment-questionnaire%e2%80%afmhaq-health-asses/